As the narrative around cannabis evolves from stigma to solution, two leading players, CBD (cannabidiol) and CBG (cannabigerol), are creating buzz without the euphoric “high.” These non-psychoactive cannabinoids are reshaping our understanding of cannabis’s role in wellness. So, what exactly is CBG and how does it differ from CBD? Let’s take a closer look at the wonders of CBD and CBG, shedding light on their potential to revolutionize health care.
What is CBG?
CBG, or cannabigerol, plays a pivotal role in the cannabis plant’s chemistry, often referred to as the “starting point” of other cannabinoids. In the early stages of the plant’s growth, CBG is present as cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), the precursor from which other cannabinoids are synthesized. Through a process of enzymatic activation, CBGA transforms, giving rise to the more familiar cannabinoids like CBD, THC, and CBC.
This unique position as a precursor makes CBG crucial in the cannabis plant’s development, which highlights its importance in the cannabis family tree. In addition, despite its conversion into other cannabinoids, CBG itself offers health benefits, making the understanding of its role both fascinating and vital for future research.
The Science Behind CBD and CBG
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a huge role in keeping balance in the human body, regulating functions such as:
- Mood
- Appetite
- Sleep
- Pain
- Immune function
Cannabis contains about 100 cannabinoids that influence the release of neurotransmitters in the brain. Several cannabinoid receptors are present in the ECS, with CB1 and CB2 being the most significant.
CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and nervous system, influencing mood and cognition, while CB2 receptors are more common in the immune system, affecting inflammation and pain.
CBD interacts indirectly with CB1 and CB2 receptors, not by binding directly to them but by enhancing the body’s endocannabinoids and affecting other receptors.
In contrast, CBG directly interacts with both CB1 and CB2 receptors.
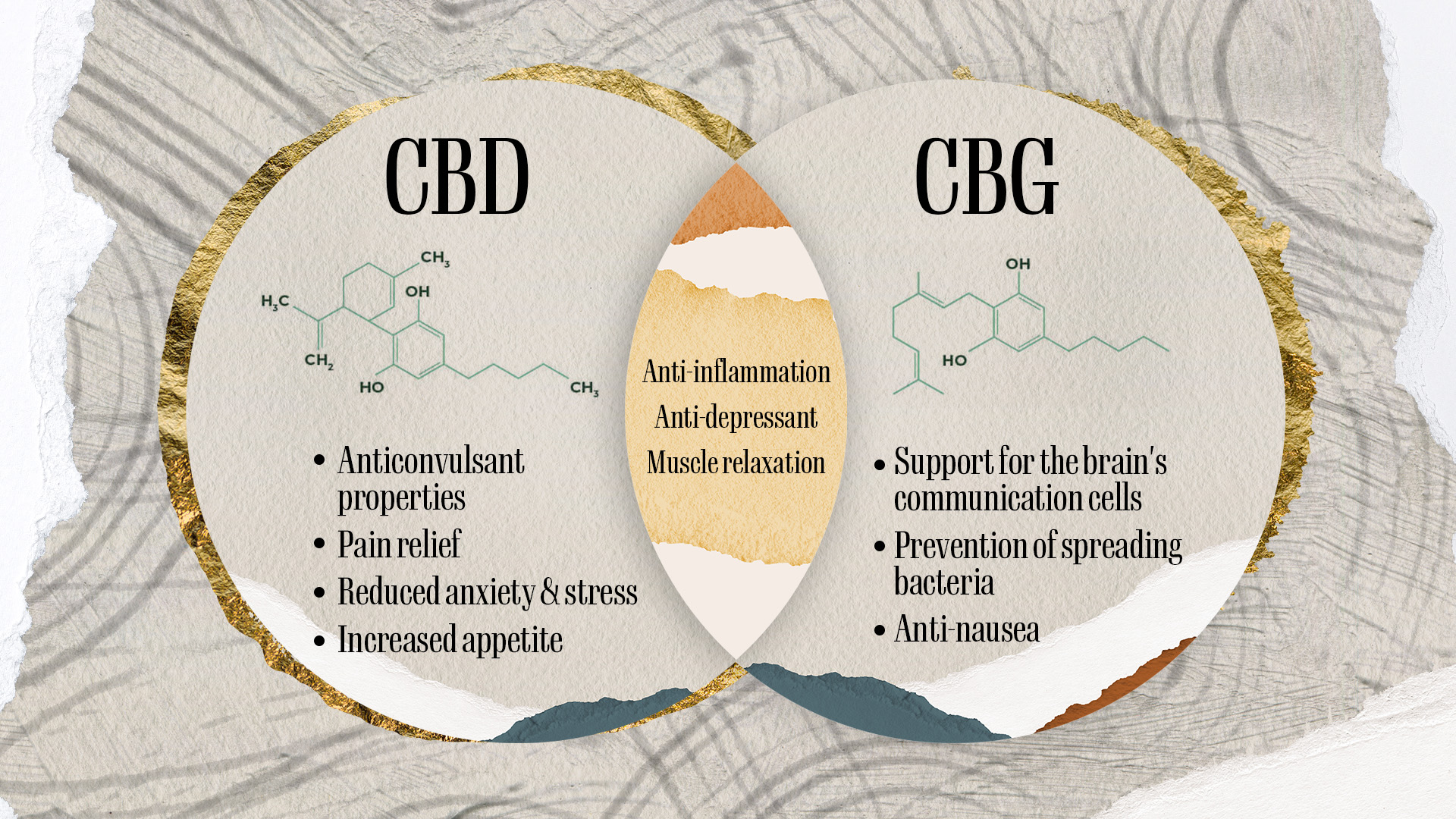
What Are the Health Benefits of CBD?
As arguably the most popular non-psychoactive cannabinoid present in cannabis, CBD has gained significant attention in the medical community for its many benefits, including:
- Anti-inflammatory Properties
- Addiction Treatment and Smoking Cessation
- Epilepsy Treatment
- Potential Benefits for Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Anxiety Disorders
Exploring the Benefits of CBG
CBG, though not as widely known or abundant as CBD, has emerged with significant healing potential, including:
Neuroprotective Properties: CBG has neurological benefits for various disorders due to its ability to:
- Protect neurons
- Reduce brain inflammation
- Promote cell repair
This may help conditions like Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis (MS).
Anti-inflammatory Effects: CBG’s interaction with the ECS could offer new treatment avenues for:
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
- Chron’s Disease
- Ulcerative Colitis
By reducing gut inflammation and promoting the healing of intestinal cells, CBG could significantly improve the quality of life for people with symptoms of these debilitating conditions.
What Are the Major Differences Between CBD and CBG?
As interest in cannabinoid therapies grows, understanding the significant differences between CBD and CBG is crucial.
Abundance
CBD is more commonly found in cannabis and is well-studied. On the flip side, CBG is rarer, comprising less than 1% of most strains. This rareness is because CBG is a precursor to other cannabinoids like CBD and THC.
Research
There is a wealth of research on CBD, highlighting its benefits for conditions such as epilepsy and anxiety. Conversely, CBG research is still technically in its infancy, but so far, it has indicated the possibility for neuroprotection, anti-inflammation, and antibacterial uses.
Effects on the Body
CBD influences the body indirectly, supporting the ECS without causing psychoactive effects. CBG, however, directly interacts with CB1 and CB2 receptors, suggesting reasons for its potent therapeutic effectiveness.
Overall, while CBD is widely recognized and researched, CBG still has a lot to offer with its unique features and prospective medical uses.
The Bottom Line
In wrapping up our exploration of CBD and CBG, it’s clear these cannabinoids are more than just buzzwords in the natural health world. They offer a beacon of hope for various health concerns, without the psychoactive effects traditionally associated with cannabis.
Whether seeking relief from chronic conditions like anxiety or looking for a natural supplement, CBD and CBG present promising options. The future of these compounds is bright, as ongoing studies and growing acceptance pave the way for new therapeutic possibilities.
Note: The content on this page is for informational purposes only and is not intended to be professional medical advice. Do not attempt to self-diagnose or prescribe treatment based on the information provided. Always consult a physician before making any decision on the treatment of a medical condition.
The post CBD vs. CBG appeared first on Cannabis Central.













